

Our volume calculator requires that you insert the diameter of the base. In many school formulas the radius is given instead, but in real-world situations it is much easier to measure the diameter instead of trying to pinpoint the midpoint of the circular base so you can measure the radius. You need two measurements: the height of the cylinder and the diameter of its base. Volume - Rectangular Prisms Table (Advanced) Using the table, students find the volume of various boxes and color the illustrations based on the results.
This worksheet uses decimals in one, two, or all three dimensions. The volume formula for a cylinder is height x π x (diameter / 2) 2, where (diameter / 2) is the radius of the base (d = 2 x r), so another way to write it is height x π x radius 2. Students use the formula for finding volume of a rectangular prism. To calculate the volume of a tank of a different shape, use our volume of a tank calculator. By designating one dimension as the rectangular prism's depth or height, the multiplication of the other two gives us the surface area which then needs to be multiplied by the depth / height to get the volume. They are usually easy to measure due to the regularity of the shape.

To calculate the volume of a box or rectangular tank you need three dimensions: width, length, and height. From cubes and rectangular prisms to cylinders and composite shapes, our volume worksheets will teach your. With plenty of activities and fun illustrations included, these worksheets help children learn in an interactive way.
IRREGULAR RECTANGULAR PRISM VOLUME HOW TO
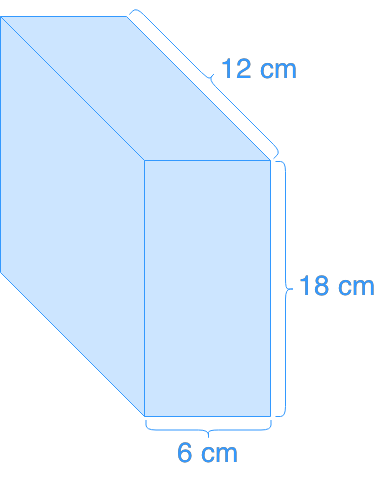
To find the volume of a rectangular box use the formula height x width x length, as seen in the figure below: irregular bezel shapes than in VIA: 26 quadrangular and four irregular shapes out of 44 seal designs with a recognisable bezel shape have been found in. With our volume worksheets, you can easily understand how to do calculations for different parameters of a 3D shape. For this type of figure one barely needs a calculator to do the math. It is the same as multiplying the surface area of one side by the depth of the cube. The only required information is the side, then you take its cube and you have found the cube's volume. The volume formula for a cube is side 3, as seen in the figure below: air conditioning calculations), swimming pool management, and more. Volume calculations are useful in a lot of sciences, in construction work and planning, in cargo shipping, in climate control (e.g.
The equation for calculating the volume of a rectangle is shown below: volume length × width ×. It is bounded by six faces, three of which meet at its vertices, and all of which are perpendicular to their respective adjacent faces. The result is always in cubic units: cubic centimeters, cubic inches, cubic meters, cubic feet, cubic yards, etc. A rectangular tank is a generalized form of a cube, where the sides can have varying lengths. All measures need to be in the same unit. Below are volume formulas for the most common types of geometric bodies - all of which are supported by our online volume calculator above. Examples of volume formulae applicationsĭepending on the particular body, there is a different formula and different required information you need to calculate its volume.Kern, James R Bland,Solid Mensuration with proofs, 1938, p.81' for the name truncated prism, but I cannot find this book. (I integrated the area of the horizontal cross-sections after passing the first intersection with the hyperplane at height $h_1$ these cross-sections have the form of the base triangle minus a quadratically increasing triangle, then after crossing the first intersection at height $h_2$ they have the form of a quadratically shrinking triangle)ĭo you know of an elegant proof of the volume formula? I was also able to prove this formula myself, but with a really nasty proof. (where $A$ is the area of the triangle base) online, but without proof. I needed to find the volume of what Wikipedia calls a truncated prism, which is a prism (with triangle base) that is intersected with a halfspace such that the boundary of the halfspace intersects the three vertical edges of the prism at heights $h_1, h_2, h_3$.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
